By Eloise Phipps
By Eloise Phipps
Imagine the scene: it is the dead of night, and you are engaged on a dangerous mission. You are tense, alert for any noise. You must complete your task without being seen, or risk the shame and humiliation of failure… but it is not a pleasant undertaking!
Your mission? A critical matter of honour. To dispose of your family’s cassava peelings – not with the rest of your household waste, but smuggled into the murky depths of the pit latrine. Why?
“The stigma about cassava is mostly among the Kikuyu people of central Kenya,” explains Henry Ngugi, Kenyan scientist and former Maize Pathologist for Latin America at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). “Traditionally, the Kikuyu are very proud, and self-sufficiency in basic needs such as food is an important factor in this. That is, you cannot be proud if you cannot feed yourself and your family. Now, the other part of the equation regarding cassava is that, traditionally, cassava was eaten during seasons of severe food shortages. It is a hardy and drought-tolerant crop so it would be available when the ‘good food’ was not. This also meant that it was associated with hunger and poverty – inability to feed oneself.”
“Another factor that may have played a role in the way the Kikuyu view cassava is that some of the traditional cultivars produced high levels of cyanide and were toxic [if not properly cooked], so as a crop it was not very highly regarded to start with. Improved cultivars have been bred to remove this problem. But because of these issues, many people would not want their neighbours to know they were so hungry they had to rely on cassava, and would go to great lengths to conceal any evidence!”
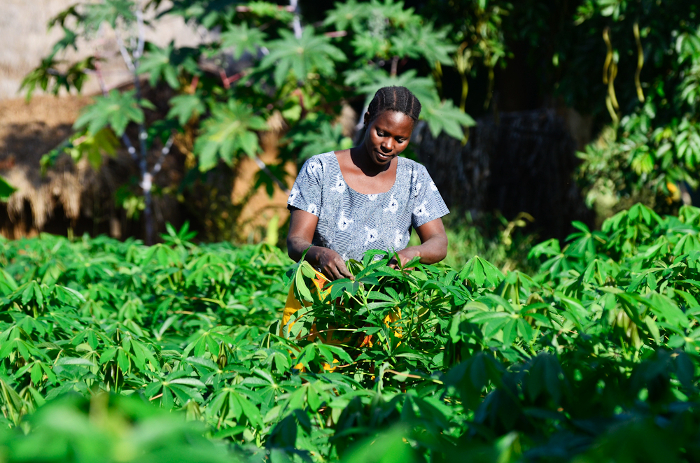

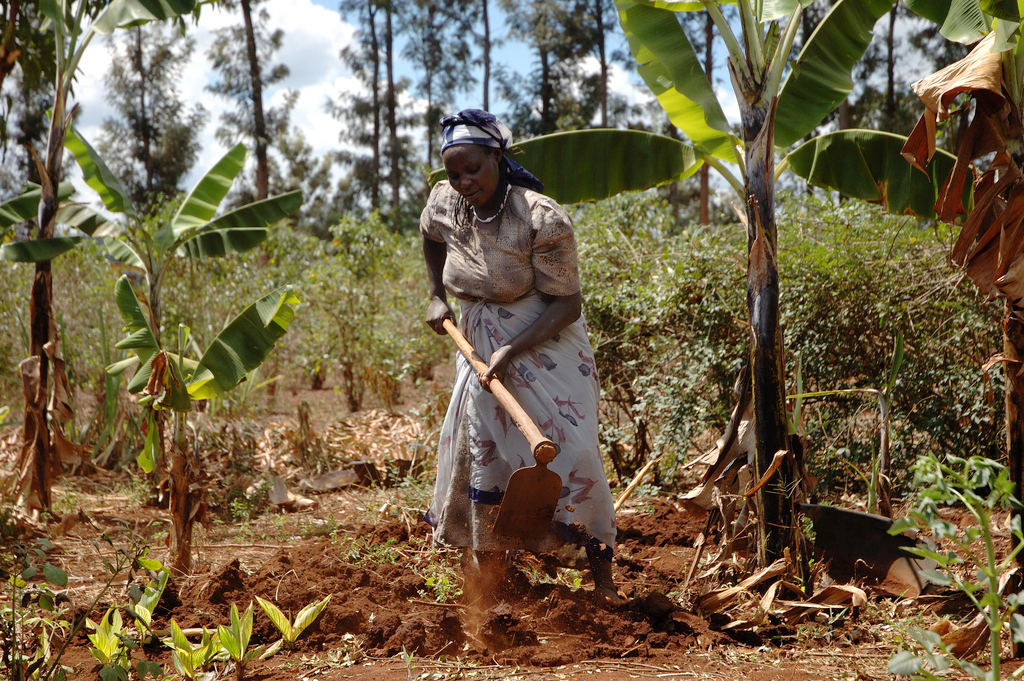
The story is not the same everywhere: graceful and strong, this farmer tends her field of cassava, in the village of Tiniu, near Mwanza, northern Tanzania.
Opening up for Open Access Week
This year, 20–26 October is Open Access Week, a global event celebrating, promoting and sharing ideas on open access – that is, making research results, including both publications and data, freely and publicly available for anyone to read, use and build upon. Even more exciting for us, this year’s theme is ‘Generation Open’, reflecting the importance of students and researchers as advocates for open access – a call that falls on fertile ground at the Generation Challenge Programme (video below courtesy of UCMerced on YouTube).
We at GCP have been reflecting this week on different virtues of openness and transparency, and the perils of shame and secrecy. But before we go on, we’re sticking with cassava (carrying over from World Food Week!) but crossing the globe to China to celebrate the latest open-access publication to join the GCP parade. ‘Cassava genome from a wild ancestor to cultivated varieties’ by Wang et al is still practically a newborn, published on the 10th of October 2014.
The article presents draft genome sequences of a wild ancestor and a domesticated variety of cassava, with additional comparative analyses with other lines. It shows, for example, that genes involved in starch accumulation have been positively selected in cultivated cassava, and those involved in cyanogenic (ie, cyanide-producing) glucoside formation have been negatively selected. The authors hope that their results will contribute to better understanding of cassava biology, and provide a platform for marker-assisted breeding of better cassava varieties for farmers.
The research was carried out by a truly international team, led by scientists from the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agriculture Sciences (CATAS) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Authors Wenquan Wang of CATAS and Bin Liu of CAS are delighted that their publication will be freely available, particularly in a journal with the prestige and high impact of the Nature family. As they observe, the open access to the paper will spread their experience and knowledge quickly to every corner of China and of the world where people have internet connections.
The work incorporated and partially built upon previous work mapping the cassava genome, which was funded by GCP in our project on Development of genomic resources for molecular breeding of drought tolerance in cassava (G3007.03), led by Pablo Rabinowicz, then with the University of Maryland, USA. This provides a perfect example of the kind of constructive collaboration and continuation that open access and sharing of research results can facilitate: by building on what has already been done, rather than re-inventing the wheel or working in isolation, we share, disseminate and amplify knowledge more rapidly and efficiently, with win–win outcomes for all involved.
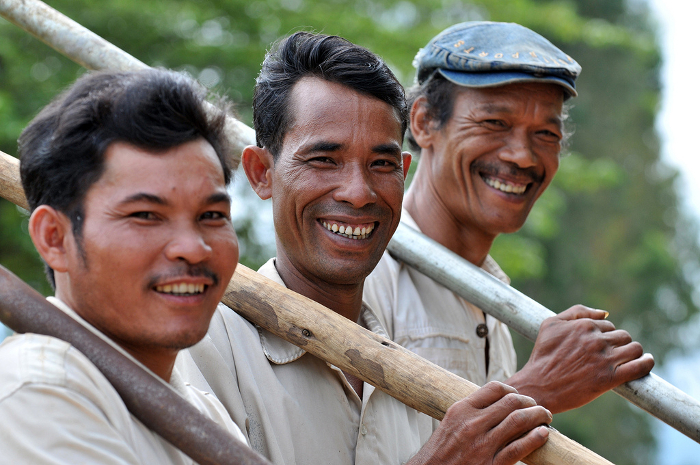

Cassava farmers in Vietnam.
One thing that makes the latest research even more special is that it was published in Nature Communications, which marked Open Access Week by going 100 percent open access from the 20th of October, making it an open-access flagship within the Nature Publishing Group – a clear indicator of the ever-increasing demand for and credibility of open-access publishing. We congratulate all of our open-access authors for making their work publicly available, and Nature Communications for its bold decision!
A matter of perspective: turning shame to pride and fears to opportunities

No shame here: a little girl clutches a cassava root in Kenya.
Of course, human beings worrying about their social status is old as humanity itself and nothing new. Food has never been an exception as an indicator. Back in mediaeval Europe, food was a hugely important status symbol: the poor ate barley, oats and rye, while only the rich enjoyed expensive and prestigious wheat. Although our ideas about what is luxurious have changed – for example, sugar was considered a spice thanks to its high cost – rare imported foods were something to boast about just as they might be today.
But why are we ashamed of eating the ‘wrong foods’ – like cassava – when we could take pride in successfully feeding our families? Many of the things we tend to try to hide are really nothing to be ashamed of, and a simple change in perspective can turn what at first seem like weaknesses into sources of pride (and there are two sides to the cassava saga, as we shall see later).
Throughout its existence, GCP has been characterised by its openness and transparency. We have worked hard to be honest about our mistakes as well as our successes, so that both we and others can learn from them. The rewards of this clear-eyed approach are clearly noted in our Final External Review: “GCP has taken an open and pro-active attitude towards external reviews – commissioning their own independent reviews (the case of the current one) as well as welcoming a number of donor reviews. There have been clear benefits, such as the major governance and research reforms that followed the EPMR [External Programme and Management Review] and EC [European Commission] Reviews of 2008. These changes sharply increased the efficiency of GCP in delivering benefits to the poor.”
Transparent decision-making processes for determining choices of methods have also improved the quality of our science, while open, mutually respectful relationships – including open data-sharing – have underpinned our rich network of partnerships.
One aspect of this open approach is, of course, our commitment to open access. All of our own publications are released under Creative Commons licences, and we encourage all GCP grant recipients to do the same, or to pursue other open-access options. When exploring our research publications you will note that many are directly available to download. Our website will act as an archive for the future, ensuring that GCP publications remain online in one place after GCP’s closure in December this year. See our Global Access Policy and our policy on data-sharing.
“Open access journals are just terrific,” says Jean-Marcel Ribault, Director of GCP. “It’s great to enable access to publications, and it’s important to promote sharing of data and open up analysis too. The next big challenge is data management, and assuring the quality of that data. At the end of the day, the quality of the information that we share with others is fundamental.”
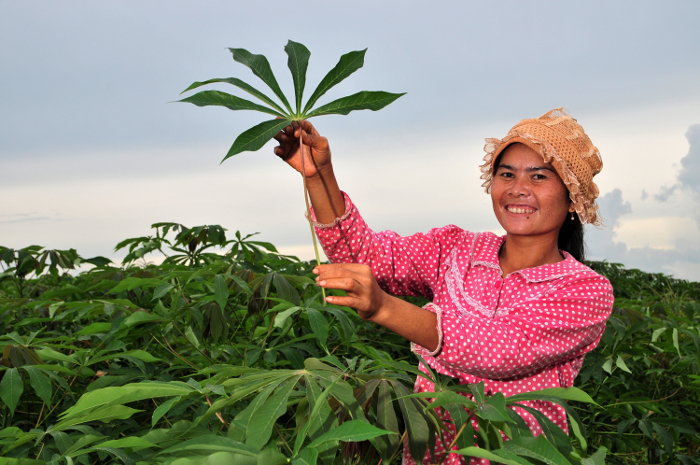

Proud in pink and polka dots: a farmer shows off a healthy cassava leaf in a plantation in Kampong Cham, Cambodia.
That’s a challenge that many other organisations are also grappling with. Richard Fulss, Head of Knowledge Management at our host CIMMYT is currently working on standards and approaches for the quality and structure of data, with the aim of implementing open access to all data within five years, meeting guidelines being put in place across CGIAR. “The issues to resolve are threefold,” he explains. “You have a licence issue, a technology issue – including building the right platform – and a cultural issue, where you need to build a culture of knowledge sharing and make open access publishing the norm rather than the exception.”
Our partners at the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) already have a strong open-access policy, and are debunking some cherished open-access myths.
It’s good to talk: saying no to secrecy
Back to cassava, and of course not everyone feels the same way about the same crop, as there are many sides to any story. In China, demand for cassava is soaring – for food, for animal feed and most of all as a raw material for starch and biofuel production – making breeding of resilient, productive cassava varieties even more important. Even within Kenya, there are those who are quicker to see the crop’s virtues. The Luhya people of western Kenya often mix cassava with finger millet or sorghum to make flour for ugali (a stiff porridge or dough eaten as a staple food in vast swathes of Eastern and Southern Africa). As Henry explains “one reason was that such ugali ‘stayed longer in the stomach’ in literal translation from local parlance meaning it kept you full for longer – which is scientifically sound because cassava has a crude starch that takes longer to digest, and lots of fibre!”
Meanwhile, watch the delightful Chiedozie Egesi, Nigerian plant breeder and molecular geneticist, in the video below to hear all about the high potential of cassava, both as a food in itself and as a raw material to make flour and other products – something some farmers have already spotted. “Cassava can really sustain a nation… we’ve seen that it can,” he says. “You have in Nigeria now some of the Zimbabwean farmers who left Zimbabwe, got to Nigeria, and they changed from corn [maize] to cassava, because they see the potential that it has.”
The power of openness is already showing itself in the case of cassava, as well as other root, tuber and banana crops. Check out RTBMaps, an online atlas developed by the CGIAR Research Program on Roots, Tubers and Bananas (RTB), using ‘scientific crowdsourcing’ to combine data on a wide range of variables, shared by many researchers, in a single map. Putting all that information together can help people make better decisions, for example on how to target breeding, or where disease threats are likely to be strongest. And for a sweet serving, here’s our humble contribution from Phase I to a world-favourite dessert!
We leave you with one final thought. It is not just cassava that is plagued with pride and prejudice; many foods attract high or low statuses in different regions – or even just variations of the same food. People in Asia and North America, for example, tend to prefer yellow maize, while Africans like their maize white. In fact, yellow maize still carries a powerful stigma in many parts of Africa, as this was the colour of the maize that arrived as external aid in periods of famine, oftentimes perceived in Africa as animal fodder and not human food in the countries it was sourced from. And thus yellow maize became synonymous with terrible times and the suffering and indignity of being unable to feed oneself and one’s family. Consequently, some of the famine-stricken families would only cook the yellow ‘animal-fodder’ maize in the dead of night, to avoid ‘detection’ and preserve family pride and honour.
This might at first blush appear to be a minor curiosity on colour and coloured thinking, were it not for the fact that when crops – such as sweet potato, cassava, or indeed maize – are bred to be rich in pro-vitamin A, and so provide plenty of the vitamin A that is particularly crucial for young children and pregnant women, they take on a golden yellow-orange hue. When promoting the virtues of this enriched maize in parts of Africa, it’s vital to know that as ‘yellow maize’ it would fall flat on its face, but as ‘orange maize’ or ‘golden maize’ it is a roaring success. A tiny difference in approach and label, perhaps, but one that is a quantum leap in nutritional improvement, and in ‘de-stigmatisation’ and accelerating adoption. Ample proof then that sharing details matters, and that it’s good to talk – even about the things we are a little ashamed of, thereby breathing substance into the spirit of the theme ‘Generation Open’.
Do have some of these uncomfortable but candid conversations this Open Access Week and live its spirit to the fullest every day after that! As for us here at GCP, we shall continue to sow and cultivate the seeds of Generation next for plant breeding into the future, through our Integrated Breeding Platform which will outlive GCP.

A little girl in Zambia gets a valuable dose of vitamin A as she eats her orange maize.
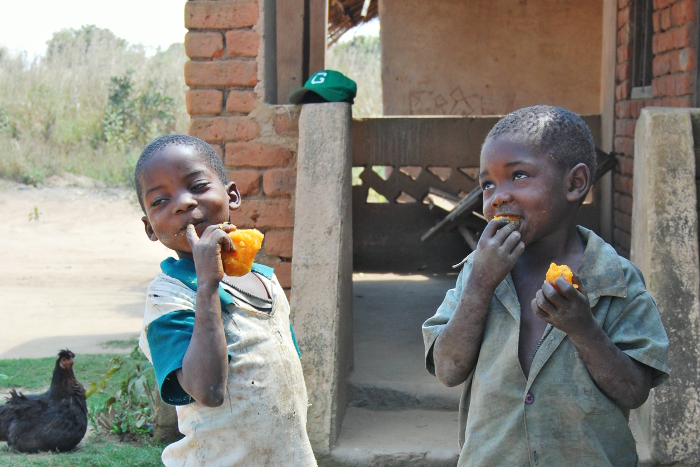

Eyes dancing with past, present or future mischief, two cheeky young chappies from Mozambique enjoy the sweet taste of orange sweet potato enriched with pro-vitamin A.
Links:
 Jurandir Magalhães (pictured), or Jura, as he likes to be referred to in informal settings such as our story today, is a cereal molecular geneticist who has been working at the Embrapa Milho e Sorgo centre since 2002. “The centre develops projects and research to produce, adapt and diffuse knowledge and technologies in maize and sorghum production by the efficient and rational use of natural resources,” Jura explains.
Jurandir Magalhães (pictured), or Jura, as he likes to be referred to in informal settings such as our story today, is a cereal molecular geneticist who has been working at the Embrapa Milho e Sorgo centre since 2002. “The centre develops projects and research to produce, adapt and diffuse knowledge and technologies in maize and sorghum production by the efficient and rational use of natural resources,” Jura explains.