Crop disease costs farmers billions of dollars each year in lost yields and inputs. For farming communities in developing countries, such losses can mean deepening poverty, food insecurity, and the resulting poor nutrition and health.
In Africa alone, it is estimated that crop pests and diseases lead to losing more than half the crops planted. Added to this, some fungal pathogens cause toxic compounds to accumulate in food. In extreme cases, crop diseases have led to widespread famine, social disruption and loss of life – the Irish Potato Famine in the 19th century is a case in point.
Overcoming this reality is what motivates plant pathologists like Rebecca Nelson (pictured below, and profiled here), of Cornell University, USA. For the past quarter century, Rebecca has worked across four continents to understand the ways in which plants defend themselves against diseases.
“Pesticides are the dominant way in which pests and diseases are managed, in spite of the many downsides to this approach,” says Rebecca. “For resource-limited farmers, this is often not an option. For those who use pesticides, the health impacts hit harder in the tropics, where protective clothing is not the norm. That’s why we’re trying to understand how plants naturally defend themselves, so that we can then tap into this, and learn from nature to breed crops that are resistant to disease.”
With this premise and funding from GCP, Rebecca collaborated with an interdisciplinary international team from USA, The Philippines, Indonesia and Kenya to identify genes associated with disease resistance in maize and rice. Although the project itself ended in 2009, that was far from the end of the story. In many ways, the end of the GCP project was in fact the beginning of life-changing chapters that followed. Thus far, the project has led to several locally developed disease-resistant varieties of rice in Indonesia and maize in Kenya.
We now already know quite a lot about the genetic architecture of several critical diseases, and this knowledge is enough for us to get started on improving the efficiency of resistance breeding”
Dissecting resistance – the genie in the genes
To understand the genetic reason behind resistance, Rebecca and her team used a range of genetic tools to dissect various forms of genetic resistance, understand the mechanisms that the plants use to reduce pathogen success, and identify the genes that provide resistance.
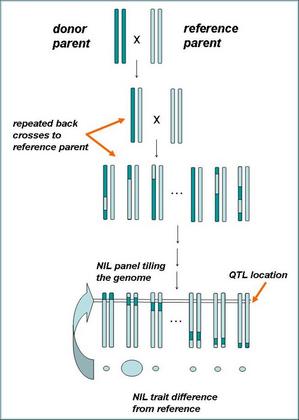
NILS explained: To create a near-isogenic line, a plant with the phenotype of interest is crossed with a standard line of the same plant. The F1 (1st filial) generation is thereafter selfed (ie, crossbred within itself) to produce the F2 (2nd filial) generation.
“There has been a lot of work done on sequencing the genomes of rice and maize, so we tapped into this work and combined our team expertise in genetics, pathology and plant breeding to help identify these disease-resistance genes,” says Rebecca. “We used recombination breeding and other genetic techniques to dissect the genomes and identify specific regions that convey disease resistance. We now already know quite a lot about the genetic architecture of several critical diseases, and this knowledge is enough for us to get started on improving the efficiency of resistance breeding. In addition, we’re identifying the genes and the ways they work, so as to interrupt pathogenesis [the manner in which a disease develops]. This involved breeding near-isogenic lines of rice and maize with the genes of interest, infecting these plants with a disease of interest, and monitoring their resistance in the field.”
Identifying genes responsible for resistance
Through this process, the team identified several genomic regions and specific genes responsible for protecting resistant rice plants against rice blast and sheath blight and resistant maize plants against northern and southern leaf blight, grey leaf spot and ear rot.
An underlying objective of the project was to also investigate if some of these genes were responsible not for just one specific disease, but for multiple diseases.
“We were intrigued by the idea of multiple disease resistance, because farmers face a range of diseases in their fields. In maize, we identified a gene associated with resistance to three diseases – southern leaf blight, northern leaf blight and grey leaf spot.”
While the team found several gene loci in both maize and rice that provide resistance to more than one disease, they have so far found little cross-benefit from the work on the two crops. But from their research they have ‘handles’ on the rich diversity of resistance loci in each of the two crops.
“Plant breeders will be able to use this information to breed crops for multiple disease resistance, increasing the security of the crop and farmers’ livelihoods,” says Rebecca.
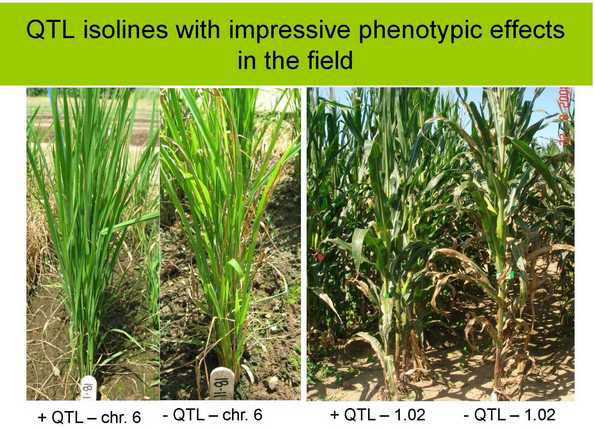
A 2008 update: a slide from Rebecca’s presentation at the GCP General Research Meeting in September of that year.
Working with that great group of people and being a part of the larger GCP family, which comprises of an amazing talent pool, was really valuable.”
Collaborating with old friends, and new
Rebecca credits her collaborators and support from the GCP family for the success of the project, saying none of the outcomes could have been achieved without everyone playing their part. “Working with that great group of people and being a part of the larger GCP family, which comprises of an amazing talent pool, was really valuable. I really appreciated that GCP supported my work at a time when I was making a transition in my career. GCP gave me and my team time and inspiration to find our feet. All of our labs are now well established, and we have since been able to diversify our funding sources.”
Project scientists from the Kenya Agricultural Research Institute (KARI) and the Indonesian Centre for Agricultural Resources Research and Development (ICABIOGRAD) reflect the involvement of country agricultural research programmes. Other partners included the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) and four universities: Bogor Agriculture University in Indonesia and Colorado State, Cornell and North Carolina State Universities, all in USA.
A highlight of the project for Rebecca was reconnecting with old colleagues at IRRI, where she had previously worked for eight years. “It was great to involve my IRRI mentor, Hei Leung, and our collaborator Jan Leach, as well as several other IRRI people whom I worked with on several rice disease-resistance projects. It was also great to involve Masdiar Bustamam of ICABIOGRAD. My team at IRRI had worked with her laboratory as she was getting it started. It was such a pleasure to see how far she and her lab had come since our earlier collaboration. They were able to make a significant contribution to the project in advancing the understanding of inheritance of rice blast and sheath blast resistance, and they developed germplasm that has really good resistance to these diseases.”
Having a limited background in maize research before the project began, Rebecca was grateful for her close collaboration with KARI’s James Gethi, who was a lead researcher in Kenya. At the time of the proposal, James was a recent Cornell graduate who was returning home to contribute to his nation’s crop-research capabilities.
“James and I were both getting our maize programmes going and the support was terrific for our labs and for our collaboration. We’ve continued to work together since our GCP project wrapped up.”

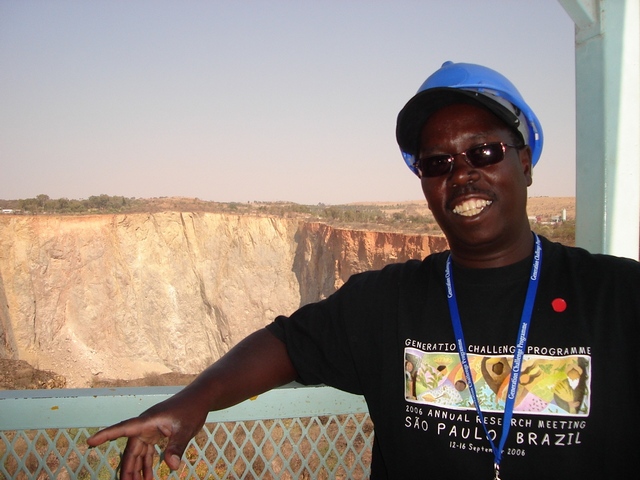
A partnership of long standing: Rebecca (left) on a field visit to Kenya in September 2006. On the right is John Okalembo of Moi University, with James Gethi behind the camera.
You can’t see it, you can’t taste it, you can’t feel it. The population is being poisoned without knowing about it.”
Continuing projects, tracking a silent cereal killer, and spreading a positive epidemic
One such project, which Rebecca and James have worked tirelessly on, is understanding genetic resistance to aflatoxins in maize. “We were travelling through Kenya together in 2005 when there was an aflatoxin outbreak,” remembers Rebecca. “Ever since, we’ve been obsessed with the problem.”
Aflatoxin is the most carcinogenic natural substance known. It is produced by species of fungi, especially Aspergillus flavus, which can colonise and contaminate grain before harvest or during storage. Maize is particularly susceptible to infection during drought, or when it is attacked by insects, or improperly stored. In 2004, 125 people died in Kenya after eating maize with very high aflatoxin levels.
“This food-safety problem is rigorously and carefully managed in developed countries but less so in cash-strapped developing nations,” says Rebecca. “In tropical countries where maize and groundnuts are often grown under stress and stored under suboptimal conditions, it is a huge problem. Yet you can’t see it, you can’t taste it, you can’t feel it. The population is being poisoned without knowing about it.”
Rebecca and James spent years trying to get support for their work on aflatoxin – the silent cereal killer – and trying to get funding for a graduate student who could take a lead. They made headway while Rebecca was on sabbatical at the Biosciences eastern and central Africa (BecA) Hub in Nairobi. BecA eventually received a major grant from Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO), and Rebecca says a strong team is now tackling the issue.
We’re indebted to GCP for bringing us together to tackle cereal diseases”
“One of our big goals was to support a promising young talent named Samuel Mutiga. I’m delighted to say that he is just finishing his PhD at Cornell now, and has done some terrific work on aflatoxin in collaboration with James and BecA.”
Samuel is one of several PhD students at Cornell who are passionate about improving food safety in Africa by beating the aflatoxin problem. “One American students is working with a Kenyan student in Nairobi to develop an improved spectroscopic grain sorter for people processing their maize at small grain mills. This will allow them to remove the toxic kernels before they mill and eat the grain, something that cannot be done visually.”
Rebecca says it’s “exciting to see this new generation take on this huge challenge. There are more scientists who are coming on board and sharing their expertise. James and I are gratified that we helped ‘infect’ these people with the conviction that something needs to be done and can be done. We’re indebted to GCP for bringing us together to tackle cereal diseases.”
Links
- For more on Rebecca’s work, see her profile | Project Briefs 2008, p 10 | Project Abstracts 2008 p 18
- For a snapshot of the beginning, flip to page 17 – A hopeful quest
- See also Rebecca’s slides below in 2007 and 2008