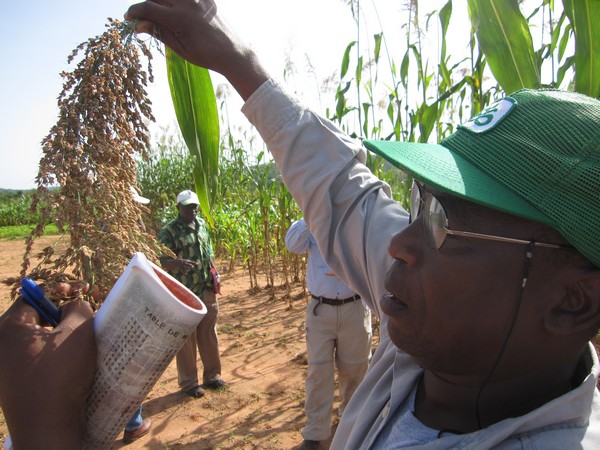
After getting a good grounding on the realities of groundnut research from Vincent, our next stop is East Africa, Tanzania, where we meet Omari Mponda (pictured). Omari is a Principal Agricultural Officer and plant breeder at Tanzania’s Agricultural Research Institute (ARI), Naliendele, and country groundnut research leader for the Tropical Legumes I (TLI) project, implemented through our Legumes Research Initiative. Groundnut production in Tanzania is hampered by drought in the central region and by rosette and other foliar diseases in all regions. But all is not bleak, and there is a ray of hope: “We’ve been able to identify good groundnut-breeding material for Tanzania for both drought tolerance as well as disease resistance,” says Omari. Omari’s team are also now carrying their own crosses, and happy about it. Read on to find out why they are not labouring under the weight of the crosses they carry…
…we have already released five varieties…TLI’s major investment in Tanzania’s groundnut breeding has been the irrigation system… Frankly, we were not used to being so well-equipped!”
Q: How did you go about identifying appropriate groundnut-breeding material for Tanzania?
A: We received 300 reference-set lines from ICRISAT [International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics], which we then genotyped over three years [2008– 2010] for both drought tolerance and disease resistance. After we identified the best varieties, these were advanced to TLII [TLI’s sister project] for participatory variety selection with farmers in 2011–2012, followed by seed multiplication. From our work with ICRISAT, we have already released five varieties.

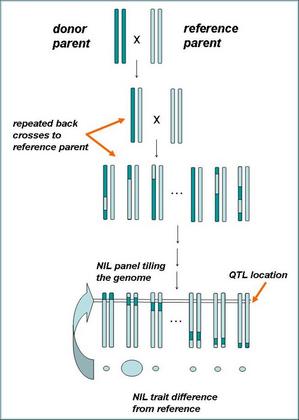
Harvesting the groundnut reference-set collection at Naliendele. A ‘reference set’ is a sub-sample of existing germplasm collections that facilitates and enables access to existing crop diversity for desired traits, such as drought tolerance or resistance to disease or pests.
ARI–Naliendele has also benefitted from both human and infrastructure capacity building. Our scientists and technicians were trained in drought phenotyping at ICRISAT Headquarters in India. One of our research assistants, Mashamba Philipo, benefitted from six-month training, following which he advanced to an MSc specialising in drought phenotpying using molecular breeding. In his work, he is now using drought germplasm received from ICRISAT. In terms of laboratory and field infrastructure, the station got irrigation equipment to optimise drought-phenotyping trials. Precision phenotyping and accurate phenotypic data are indispensable for effective molecular breeding. To facilitate this, ARI–Naliendele benefitted from computers, measuring scales, laboratory ware and a portable weather station, all in a bid to assure good information on phenotyping. But by far, TLI’s major investment in Tanzania’s groundnut breeding has been the irrigation system which is about to be completed. This will be very useful as we enter TLIII for drought phenotyping.
For us, this is a big achievement to be able to do national crosses. Previously, we relied on ICRISAT…we are advancing to a functional breeding programme in Tanzania… gains made are not only sustainable, but also give us independence and autonomy to operate..We developing-country scientists are used to applied research and conventional breeding, but we now see the value and the need for adjusting ourselves to understand the use of molecular markers in groundnut breeding.”

Flashback to 2010: Omari (right), with Hannibal Muhtar (left), who was contracted by GCP to implement infrastructure improvement for ARI Naliendele, and other institutes. See http://bit.ly/1hriGRp
Q: What difference has participating in TLI made?
A: Frankly, we were not used to being so well-equipped, neither with dealing with such a large volume as 300 lines! But we filtered down and selected the well-performing lines which had the desired traits, and we built on these good lines. The equipment purchased through the project not only helped us with the actual phenotyping and being able to accurately confirm selected lines, but also made it possible for us to conduct off-season trials.
We’re learning hybridisation skills so that we can use TLI donors to improve local varieties, and our technicians have been specifically trained in this area. For us, this is a big achievement to be able to do national crosses. Previously, we relied on ICRISAT doing the crosses for us, but we can now do our own crosses. The difference this makes is that we are advancing to a functional breeding programme in Tanzania, meaning the gains made are not only sustainable, but also give us independence and autonomy to operate. Consequently, we are coming up with other segregating material from what we’ve already obtained, depending on the trait of interest we are after.
Another big benefit is directly interacting with world-class scientists in the international arena through the GCP community and connections – top-rated experts not just from ICRISAT, but also from IITA, CIAT, EMBRAPA [Brazil], and China’s DNA Research Institute. We have learnt a lot from them, especially during our annual review meetings. We developing-country scientists are used to applied research and conventional breeding, but we now see the value and the need for adjusting ourselves to understand the use of molecular markers in groundnut breeding. We now look forward to TLIII where we expect to make impact by practically applying our knowledge to groundnut production in Tanzania.
Interesting! And this gets us squarely back to capacity building. What are your goals or aspirations in this area?
A: Let us not forget that TLI is implemented by the national programmes. In Africa, capacity building is critical, and people want to be trained. I would love to see fulltime scientists advance to PhD level in these areas which are a new way of doing business for us. I would love for us to have the capacity to adapt to our own environment for QTLs [quantitative trait loci], QTL mapping, and marker-assisted selection. Such capacity at national level would be very welcome. We also hope to link with advanced labs such as BecA [Biosciences eastern and southern Africa] for TLI activities, and to go beyond service provision with them so that our scientists can go to these labs and learn.
There should also be exchange visits between scientists for learning and sharing, to get up to date on the latest methods and technologies out there. For GCP’s Integrated Breeding Platform [IBP], this would help IBP developers to design reality-based tools, and also to benefit from user input in refining the tools.
Links
- Groundnuts – Research | Research products | Videos | Blogposts | InfoCentre | Slides
- Legumes – Research Initiative | InfoCentre (including for groundnuts)
- Integrated Breeding Platform (IBP) – What’s it all about? | Introduction blogpost | Other IBP blogposts
- TLIII – Tropical Legumes III Project
- ‘Naliendele’ demystified: what does the name mean?
SLIDES by Omari on groundnut research and research data management in Tanzania